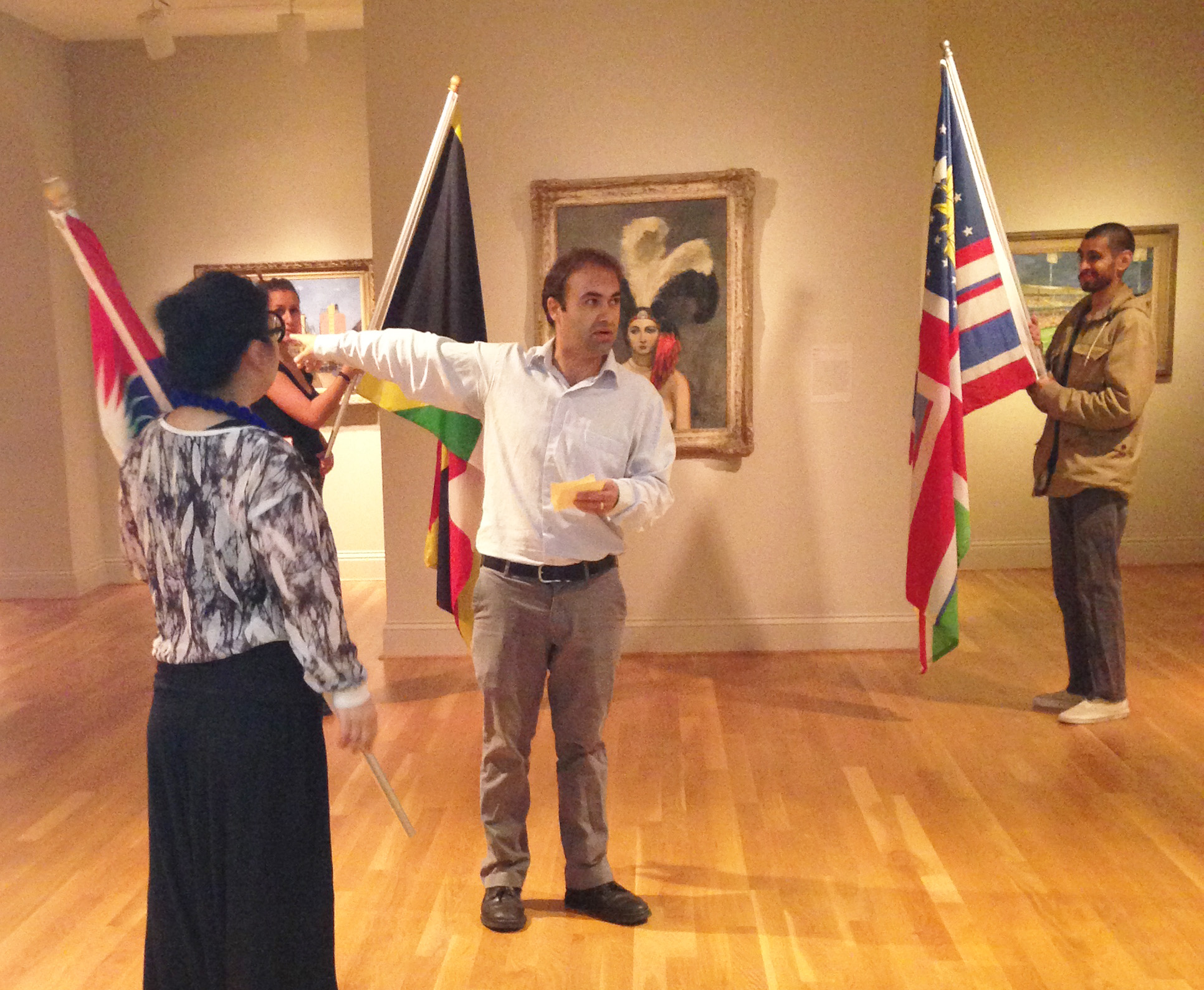
On October 27, artist Pedro Lasch will premiere his work Abstract Nationalism/National Abstraction: Anthems for Four Voices at The Phillips Collection as part of the International Forum Weekend in Washington. In this audio-visual performance, national anthems of specific countries are sung in the language of the country listed alphabetically after it in the World Almanac.
In a six part blog series, Curatorial Intern Lauren Reuter asks the artist about this work and how it fits into the Phillips, art, and politics. Read Part 1 here, and Part 2 here.
What has been your experience in creating this project? What has been the response to the project from institutions you’ve connected with?
To me, it’s a bit like Federico Fellini, the Italian filmmaker, once said: “I don’t make a movie so that I can go watch it in the theater. I make it because I love every stage of making the movie.” It’s the process. Of course you still care about the final thing and that’s what people get to see, but for the artist and those involved in the process of making—the staff at the Phillips, people at the embassies—that’s what we enjoy. At least that’s what I think we should enjoy. It’s through our engagement with embassies, cultural institutes, potential partners in DC that we’ve been testing a lot of ideas: Does the work resonate? Do people want to connect with it? The answer to that has been a pretty overwhelming yes. People are into it, they’re ready to engage. That’s great, but then it gets more complicated. Each embassy has different protocols, and some forms of this project literally break those protocols. Some countries have laws that forbid them from doing certain things with their flags and their anthem. So we have been very open about what we’re trying to do and making sure that people don’t misunderstand; there’s humor in the project, but not parody. If an embassy staff person sees it as a parody of their country, it would be a disaster for me. That’s not what it is about. It’s very sensitive stuff, though many people in the art world don’t think it is.
The first thing you have to acknowledge when talking with embassies is that people there are hired to represent their country. And so what we’ve learned from these conversations is that people are ready and interested to engage with this notion of multinationalism and multlingualism. Many representatives of these embassies themselves speak three or four languages. But when it comes to actually presenting the work in the actual embassy itself as a building, things can get complicated. You may have all the cultural [representatives] interested in doing the work, but it can’t happen because they realize that legally you can’t do it, or people worry that someone in the audience will not understand what the work is trying to do. It’s not a big surprise but it is very labor intensive. To me that’s what makes the key difference between a social practice artist or institutional critique artist and a painter who spends most of his production time in the studio and then puts his art on the wall. All these conversations, all these negotiations, all this back and forth—each element is a production of different people. If they weren’t all happening, I would feel like half of the project would be missing.